ASIF-scheme for GHG emissions of transport
The ASIF scheme was originally described in a paper prepared by the IEA on behalf of the World Bank [SCHIPPER ET AL. 2000]. It has found prominent application in recent publications of the IEA [IEA 2009, FULTON ET AL. 2009]. ASIF stands for the variables of a generic equation to calculate the GHG emissions of transport that reads:
GHG = Activity x modal Share x energy Intensity x carbon intensity of Fuel
Where:
- GHG means the GHG emissions of transport
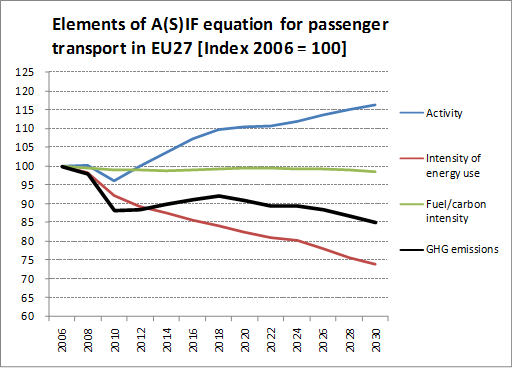
- Activity means transport performance (pkm, tkm) or vehicle-km
- Modal Share means the modal-split of passenger and freight transport
- Energy Intensity means the energy demand by mode and by fuel per pkm, tkm or Vkm
- Fuel means the carbon intensity per unit of energy demand by fuel.
The ASIF equation exists in many variants, a few applying a more aggregate structure [e.g. SCHÄFER ET AL. 2009], but in most cases differentiating some variables of the ASIF equation into more detailed variables [e.g. as already suggested by the original paper of SCHIPPER ET AL. 2000].
The single components of the ASIF equation can be deduced from the ASTRA model, estimating the total emissions of greenhouse gases from transport. In the following example, only the elements A (activity), I (energy intensity) and F (Fuel/carbon intensity) are included and modal shares (S), are omitted, so that in fact an A(S)IF approach is applied.